The name Nikon is derived from Nippon Kogaku, which literally meant "Japan Kodak", or so I thought. But several sources have informed me that "Kogaku" is merely the Japanese word for "Optical".
Apparently, long before George Eastman was born, the word "Kogaku" existed in Japanese; it was the name for a neo-Confucian school of thought, and it had the meaning "Ancient Wisdom". Later on, it became both the word for the science of optics, and also a word for technical and scientific specialties in general.
Had the name meant "Japan Kodak", as I thought, this would not have even been unique; JVC, the company that came up with the VHS videotape format, is the "Japan Victor Company". Apparently, there was a time when major U.S. trademarks were not safe in Japan.
And yet, Nikon and Kodak, although both leaders in the field of photography, seem, if anything, to be opposites. Kodak is primarily focused on products for the consumer, at least in the area of cameras, (as a major film supplier, they did very much consider the needs of professionals in that part of their business) while Nikon emphasized high-end professional gear.
One example of how Kodak focused on making photography easier for the consumer was their introduction of certain new film formats.
In 1963, they introduced Instamatic cameras, which used 126 film in special cartridges, which eliminated the need to thread film and the risk of accidentally exposing it.
Incidentally, from 1897 to 1907, Kodak manufactured a camera called the "No. 4 Cartridge Kodak". However, this did not use film contained in any kind of cartridge, it instead used 104 roll film, wound on spools with backing paper, just like 620 film or 127 film. So the Instamatic was not anticipated in the early days of photography by Kodak, at least.
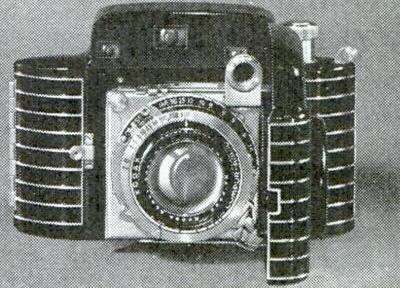
The film in an Instamatic cartridge was 35mm wide, but it had a backing sheet of paper with exposure numbers printed on it, as with 620 roll film or 127 roll film - and, as well, it did not have lots of perforations on both sides either, although like 828 film, at least originally, it did have one perforation per frame along one side. Thus, it was basically the same kind of film as previously sold by Kodak as 828 roll film, although the frame size, and hence the spacing of its limited number of perforations, was different.
Amazingly enough, shortly before the Kodak Instamatic camera came out, a California company by the name of Traid put actual Kodak 828 film in cartridges, for use with their camera, the Fotron. However, this camera offered disappointing value for money, and thus was not successful. It used a different image size than Kodak 828 cameras so that it could offer 10 photos per cartridge, as opposed to the 8 photos per roll of 828 film normally available from Kodak 828 cameras.
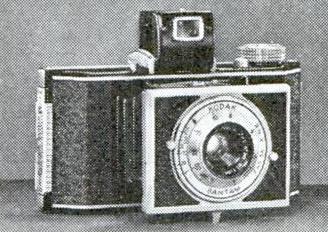
Pictured at left is the Kodak Bantam camera, and at right is the Kodak Bantam Special camera from 1936. The Kodak Bantam camera was the principal camera associated with the 828 film format.
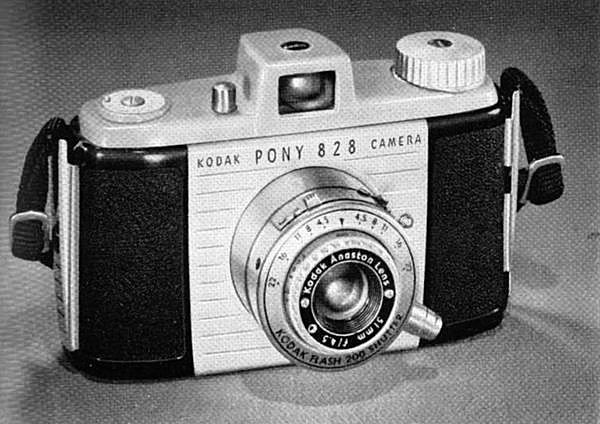

Pictured at left is the Kodak Pony 828 camera from 1949, another example of a camera that used this film format.


Given that 828 film was so closely related to standard 35mm film, it is not surprising that some of the cameras made for 828 film were closely related to those made for 35mm film.
Pictured here, therefore, is the Kodak Pony 135 camera; on the left, an example of the Model B version of that camera is shown, and on the right, a Model C version is pictured.

What about the original version of the Kodak Pony 135? It was harder for me to find an advertisement which included a picture of it; I ran across several which, under a picture of the Kodak Pony 828, also mentioned the Pony 135 in passing. However, I did finally come across an advertisement which included the picture shown at right: on the left is the Model A version of the Kodak Pony 135, standing behind a Kodak Pony 828.
Apparently, therefore, at least initially, Kodak expected 828 film to be more popular than 135 film, Kodak's designation for 35mm film for still picture photography in cartridges.
Incidentally, the f/4.5 Anaston lens was a Cooke triplet; it was Lumenized, which meant that it had an antireflection coating. With a speed of f/4.5, a simple triplet lens was an entirely reasonable and appropriate design of lens to use; even a Tessar would only be needed for a faster speed.
When 828 film was first introduced in 1935, it had one perforation per frame, with the perforations spaced 43 mm apart to allow some space between the 40 millimetre-wide frames. The 126 film in the Instamatic cartridge also had one perforation per frame, and these were apparently spaced at a distance of 34.5 mm.

While most of the Instamatic cameras made by Kodak were simple point and shoot cameras, with fixed-focus lenses, Kodak did get around to making an SLR camera that used these 126 film cartridges, as depicted at right, and, in fact, there were also such cameras made by Ricoh, Rollei, Zeiss Ikon (under their Contaflex brand), and the Keystone K 1020 (which is, according to one web site, suspiciously similar to the Mamiya Auto-Lux 35mm SLR).
The Keystone K 1020 auto-instant SLR is of particular interest because it was the first SLR to use the 126 Instamatic cartridge from Kodak; it had a large selenium light sensor on the front of the camera. However, it did not have interchangeable lenses.
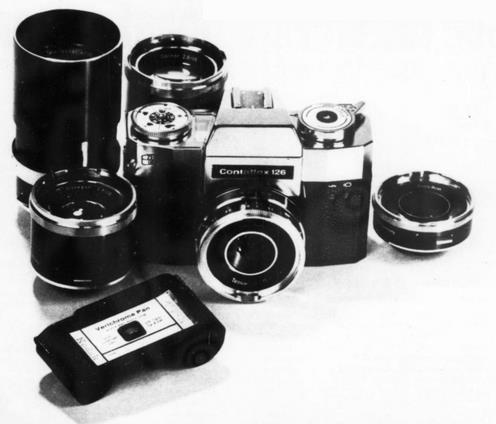

The image shown at left, from an advertisement for the Contaflex 126, by the West German firm of Zeiss Ikon, as noted (but it had also merged with Voigtländer at this time) shows how they emphasized the fact that their camera had a large assortment of interchangeable lenses available for it, bringing serious photography to the 126 cartridge.
The Kodak Instamatic Reflex used the same type of lenses as the previous Kodak Retina Reflex SLR, and thus did not opt for a focal-plane shutter. (This is not as strange as it sounds. The Kodak Instamatic Reflex camera was introduced in 1968; the Kodak Retina Reflex IV camera was sold from 1965 to 1967, so those cameras were not a long-forgotten relic of the past at the time. But there is still something strange here: if the Instamatic Reflex camera was worth making, why was the Retina Reflex discontinued: it wasn't as if 35mm film was going anywhere?) However, the conventional shutter it did have was one of the first electronic shutters to be used in a consumer camera.
The standard image size for 828 film was 40mm by 28mm, and there were only eight exposures on a roll. Since Kodak had continued to make and sell 828 film until 1985, one is tempted to ask, in order to avoid wasting film on sprocket holes, why the world's compact SLR cameras weren't made to use 828 film instead of 35mm movie film, even if the precedent of using 35mm movie film was set by the Kine Exakta?
Well, there's actually one obvious reason why not which we've already seen, the limitation to only eight exposures per roll, but if Kodak could make both 120 film and 620 film, obviously it could have sold the same kind of film as used in both 828 reels and Instamatic cartridges on reels that held 25 or 36 exposures instead of just eight.
Of course, SLR cameras using 828-style film, particularly assuming they still used the standard 828 frame size of 40mm by 28mm, would have been slightly larger: a 36mm by 24mm frame has a diagonal of about 43.266615mm, while a 40mm by 28mm frame would have a diagonal of about 48.826222mm, so a normal lens might have a focal length of 56mm in that world in order to match the 35mm SLR; however, many books on photography state that the focal length of a normal lens should nominally be the same as the diagonal of the image format, which would mean that 50mm would do for 828 film as well. On the other hand, the standard frame size for 126 film, as used in the Instamatic cartridge, was 28mm by 28mm, yielding square images, perhaps more suitable for slides; here, the diagonal would have been about 39.6mm; however, the Instamatic Reflex is fitted with a 50mm lens, not, say, a 46mm lens.
Of course, had the world unfolded this way, making SLRs with full-frame sensors would have ended up a greater challenge than it already is, as the area of the sensor would have been 29.6% larger.
Changing the frame width to something shorter than 40mm in order to keep the diagonal the same as that of the 36mm by 24mm frame of 35mm film wouldn't have allowed the use of the same lenses; since the height of a picture would still be 28mm instead of 24mm, and so lenses would require a longer back focus because the height of the reflex mirror is determined by the height of the film frame, and the thickness of the camera is determined by height of the reflex mirror, as there has to be room for it to swing upwards. But the height of a picture was 28mm on the 126 film Instamatic cartridges instead; how did the Instamatic Reflex overcome this? According to Wikipedia, as I note below, Kodak cropped the frames for 126 film during processing to 26.5 mm by 26.5 mm; while this is still larger than 24mm, perhaps there was enough extra room available, and/or the resulting vignetting was so slight as not to be noticeable.
If the format of 35mm film for still picture photography could be designed from scratch, what would have been the optimum design? Comparing the 126 Instamatic cartridge to 828 film and to regular 35 mm film started me thinking about this.
I think that one desirable characteristic of such a format would be to allow pictures to be taken with the same aspect ratios as could be taken with cameras using 120 film.
Some 120 film cameras used a 6x6 format, some a 6x7 format, and some a 6x9 format.
If we start with film that is 35 mm wide, with small perforations down one side only, which could be the same size as those used with the original 8 mm film for home movies, there should be no problem making the frame size 30 mm wide, the next larger multiple of 6 millimetres after 24 mm.
On standard 8mm film, the distance between the image frame and the edge of the film on the side with the sprockets is 2.94 mm, by one account, so this type of sprocket would allow for the 30 mm high image area to be positioned very simply; 2 mm away from the edge of the film without sprockets, and 3 mm awy from the edge of the film on the side with sprockets.
So we would want to allow frames that were 30 mm by 30 mm, 30 mm by 35 mm, and 30 mm by 45 mm.
This sounds like the film should have sprockets every 5 millimetres along its length. But film formats usually allow at least 1 millimetre between successive frames of film, and it would be wasteful to have a full 5 millimetres of space between frames.
So, to use round numbers for dimensions, I concluded that it would be appropriate to space the perforations of an improved 35 mm film for still photography at 5.2 mm intervals along the film. This would lead to 1.2 mm of space between 30 mm by 30 mm photographs, 1.4 mm of space between 30mm by 35 mm photographs, and 1.8 mm of space between 30 mm by 45 mm photographs.
4.75 mm, times eight, is 38 mm, so there is 2 mm of space between every image on a normal 35 mm camera, so even 1.8 mm is not excessive.
What about 3D cameras that take stereo pairs of images? The closest multiple of 5.2 mm to the 63 mm standard for interocular distance is twelve perforations, at 62.4 mm. So this would work with the 30mm by 30mm format that used six perforations per frame.
And, of course, the eight perforation 30 mm by 40 mm size would approximate the 4:3 aspect ratio of the original 35 mm motion picture film.
However, for some reason there are very few 6x8 medium format cameras. According to one forum post I've found, it's because the 6x6, 6x7, and 6x9 formats, instead of being 60 mm by 60, 70, and 90 mm, are really only approximations to image frame sizes originally defined in inches: 2 1/4 inches high by 2 1/4 inches, 2 3/4 inches, and 3 1/4 inches respectively.
And the diagram below shows how this came about.

The 2 1/4 by 2 1/4 format is a square format, just as 60 mm by 60 mm would be, just a bit smaller.
The original British Imperial formats are shown on the left, their metric approximations are shown in the center. The two are superimposed on the right.
Widening the format by half an inch to 2 1/4 by 2 3/4 inches means that the format is still a bit less tall than 60 mm, but it's almost exactly 70 mm wide (actually 69.85 mm wide, with the difference not being visible on the scale of the diagram), which is what led to it being called 6x7 cm format in metric.
But when the format is widened by another half an inch, then it's clearly wider than 80 mm, so that format was called 6x9 instead of 6x8. So 6x6, 6x7, and 6x9 are formats that are really equally spaced in width.
In that case, the frame sizes to be offered really ought to be, say, 27 mm high by 27 mm, 33 mm, and 39 mm in width. The perforations could be spaced 6 mm apart, leaving a 3 mm space between images on the film, but as that is a bit large, changing the spacing to 5.8 mm would mean that five perforations would leave 2 mm space between 27 mm wide images, six perforations would leave 1.8 mm space between 33 mm wide images, and seven perforations would leave 1.6 mm space between 39 mm wide images.
Or, let's leave the height of the frame at 30 mm, and space the perforations 6.4 mm apart. Five perforations are 32 mm, so 2 mm is left between frames that are 30 mm wide. Six perforations are 38.4 mm, and the frames would now be 36.667 mm wide, leaving 1.733 mm of space between frames, and seven perforations are 44.8 mm, while the frames would be 43.333 mm, leaving 1.467 mm of space between frames, still fully adequate.
The height of the image area, at 30 mm, is still a multiple of a millimetre, and the space between sprockets, at 6.4 mm, is still a multiple of a tenth of a millimetre. That one would be dealing in thirds of a millimetre in the dimensions of the frame that crops images (and the resulting space between frames would be in units of thirtieths of a millimetre, given that they result from a subtraction between thirds and tenths) would not be too much of an issue, and the film would be used more efficiently.
The diagonal of a 24 mm by 36 mm image on a conventional 35 mm camera is about 43.266615 mm. That of a 30 mm by 43.333333 mm frame would be about 52.704628 mm. or almost 1.22 times as large, and so lenses for cameras for this new film standard would have to be larger than 35 mm lenses in that proportion in order to fully cover the largest frame size offered.
Actually, though, since while this is a new format for 35mm film designed from scratch, the current 35 mm film format does already exist. So it would also be desired to take pictures which resemble those taken by those 35mm cameras, not just those taken by medium-format cameras.
A frame size of 30 mm by 45 mm, for the 3:2 aspect ratio, would involve advancing the frame by eight perforations between shots, and would leave 2.2 mm of space between images, so that would work out too; now, the lenses would have to be 1.25 times larger to accomodate that choice as well.
Since the frames are made to have the same proportions as those used with medium format cameras, presumably the focal lengths of the lenses offered should be based on those of the lenses offered for medium format cameras, but scaled down by a factor of 1.905, the proportion between 2 1/4 inches and 30 millimetres, so that the two types of cameras could take essentially the same pictures. (Of course, though, things like depth of field would differ between the two film formats, as depth of field depends on the actual size of the aperture, not its ratio to focal length.)
Thus, the normal lens on a Hasselblad has a focal length of 80mm, so presumably the focal length of a normal lens for this type of camera would be 42 mm, rather than, say, 61 mm or 63 mm if one was scaling up from the 50 mm focal length of the normal lens for a 35 mm camera based on the previous standard film format.
Here is a short table of equivalent focal lengths based on some lenses offered for the Hasselblad:
30 mm 16 mm Fisheye 40 mm 21 mm Wide-Angle 50 mm 26 mm 80 mm 42 mm Normal 100 mm 53 mm 150 mm 79 mm Portrait 250 mm 131 mm Telephoto 350 mm 184 mm 500 mm 263 mm
Some focal lengths between 100 mm and 150 mm were omitted, as apparently only special-purpose lenses were offered with focal lengths in this region.
On the other hand, if the regular 35mm camera is used as the basis, then multiplication by a factor of 1.25 becomes the conversion method, and this table would apply:
15 mm 19 mm 28 mm 35 mm 35 mm 44 mm 50 mm 63 mm 80 mm 100 mm 105 mm 131 mm 135 mm 164 mm 200 mm 250 mm
Of course, since Kodak chose to use an image height of 28 mm for 828 film, perhaps we should accept the wisdom of the decision they made with their great experience in photography, and go instead with the 27 mm image height in order to leave an adequate margin of safety.
While I don't know what the dimensions of the sprocket holes in early 828 film were, an image of modern 35mm film used to take pictures in an 828 film camera that I saw gave information on where the image area was located within the film. Perhaps the wide edge might be 11/64" while the narrow edge is 5/64", on film that is 1 3/8" wide, leaving 1 1/8" for the image height. But 5/64" is very slightly smaller than 2 mm, so that indicates that 2 mm is not an inadequate margin to leave between the image and the edge of the film.
Also, I don't have to guess at the size of the perforations in 126 film, although those peforations seem to be too large in both directions to use as a model.
But, on the other hand, it still suggests that the side with the sprockets ought to be about 5 mm wide rather than just 3 mm wide, implying that there may not really be enough space for a 30 mm image area, since 35 mm wide film may need larger sprockets to properly move it than 8 mm wide film does.
However, given that "35 mm" film is really 1 3/8" wide, instead of choosing between a 27 mm height and a 30 mm height for images, the actual "28 mm" height of images on 828 film is 1 1/8"; this is 9/8", so it is already divisible by nine, and thus can be chosen without a change.
Now, the image formats become:
Nominal Actual 120 film Actual 828-based
60 mm by 60 mm 2 1/4" by 2 1/4" 1 1/8" by 1 1/8"
60 mm by 70 mm 2 1/4" by 2 3/4" 1 1/8" by 1 3/8"
60 mm by 90 mm 2 1/4" by 3 1/4" 1 1/8" by 1 5/8"
2 1/4" by 3 3/8" 1 1/8" by 1 11/16"
So now the size of images on 120 film is simply cut in half, making it trivial to maintain the proportions. And so now a full-frame sensor would be 28.6 mm by 42.9 mm instead of 24 mm by 36 mm.
To give the desired spacing for images on the film, eight perforations presumably would equal 1 5/8 inches plus some quantity greater than 5/128ths of an inch. A spacing of 7/32" between perforations would mean that eight perforations are 1 3/4" long, allowing a minimum spacing between images of 1/8", which, although generous, is smaller than 1/4" as desired. Or one could approach closer to the ideal with 27/128" spacing between perforations reduceing the minimum spacing between images to 1/16".
During the 1930s, Agfa had introduced the Karat film cartridge; in 1966, it was inspired by Kodak's Instamatic cartridge to bring it back, adding a mechanical indication of film speed to the cartridge, a feature the 126 cartridge also had. While a number of manufacturers offered cameras that supported the Agfa Rapid System, it did not last long, at least in the North American market.

Later, starting in 1972, the Instamatic brand name was also used for a smaller cartridge containing 110 film, and Pentax made a miniature SLR camera, the Pentax Auto 110, which used that film. This camera is shown at right. However, the interchangeable lenses were all fixed focal length lenses, which sounds incredible; however, given that the camera was so small, a lens focused at "infinity" would still bring anything at any reasonable distance into sharp focus, so that could actually have made sense.
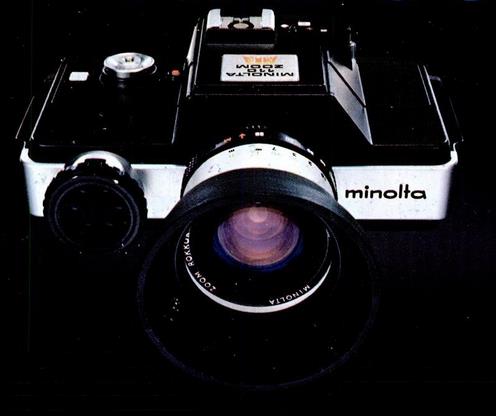

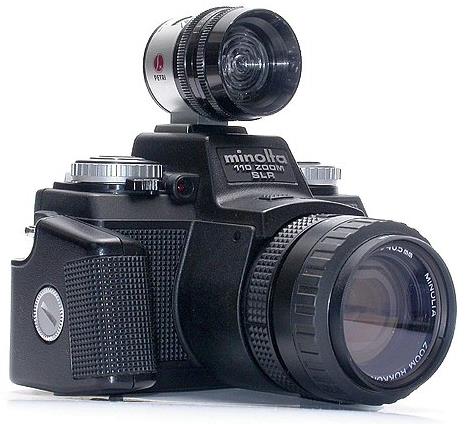
Minolta also made an SLR built around the 110 film cartridge, the Minolta 110 Zoom. Their first version, as shown at left, looked considerably different from that by Pentax...
 |
The image above is from Wikimedia Commons, licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic License, and is thus available for your use under the same terms. Its author is John Nutall. |
but subsequently, with the Minolta 110 Zoom Mark II, shown at right, with a third-party auxilliary viewfinder installed in the shoe, they decided to follow Pentax and go with a design that looked like a smaller version of a 35mm SLR.
The zoom lens on this camera is not interchangeable, but it can be focused, unlike the lenses on the Pentax camera.
The 110 cartridge indicated only one of three possible film speed values, high, medium, and low, and the film speeds assigned to these apparently changed over the life of the format!
Later, Kodak went still further in this direction with the Kodak disc camera.
35mm film, as used in the Leica and most SLR cameras, had an image area of 36mm by 24mm.
126 film had a basic image area of 28mm by 28mm, although that was usually cropped somewhat during processing; Wikipedia gives the figure of 26.5mm by 26.5mm.
110 film, introduced by Kodak in 1972, had a frame size of 17mm by 13mm. Note that cropping it by a millimetre would lead to 16mm by 12mm, with the motion picture aspect ratio of 4:3. The film itself was 16mm wide, and, like 126 film, it had one perforation per frame. These perforations were apparently 26 millimetres apart, which allowed for quite a generous spacing between frames.
The image size in the Kodak disc system was 10mm by 8mm, thus larger than that of 8mm home movies at 4.8mm by 3.5mm, or even Super 8 at about 5.8mm by 4mm.
Not only that, but the small size of the frame in the Kodak disc camera system was mitigated by another factor, a recent technical innovation on the part of Kodak.
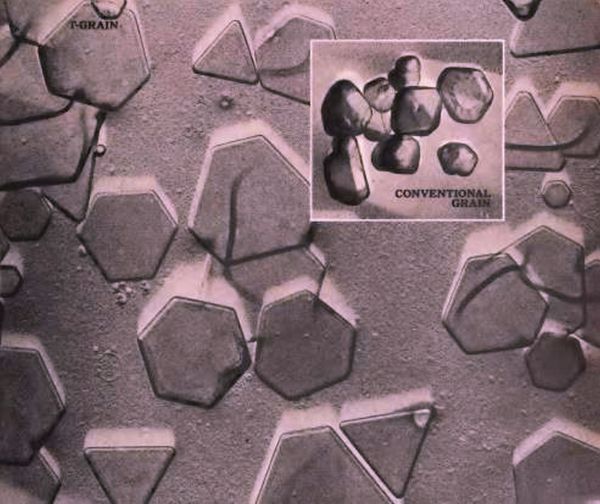

The image above, from a Kodak advertisement, shows a microphotograph of silver halide grains as modified by Kodak's T-grain process; these flat grains allowed Kodak to produce Kodacolor VR 1000 film, which, as its name suggests, had a sensitivity of ASA 1000, and they also allowed it to give Kodak disc films higher resolution to produce acceptable results with the smaller frame size. A T-grain emulsion was also used to make a version of Kodachrome with ASA 200 available.

Of course, not all film formats, only nearly all of them, were defined by Kodak. A large number of Japanese companies produced tiny cameras that used film that was 17.5 mm wide; this being half of 35 mm, so the film could easily be made from readily available 35mm film.
One such camera, the Mycro, is illustrated at right.
Similar cameras were also made that used standard 16mm film.


Of course, if one is going to talk about small cameras, it would not do to forget about the Minox. This camera used film that was 9.2 mm wide, and the image area on the film was 8 mm by 11 mm, not far from that used on the Kodak disc camera, but without the benefit of T-grain emulsions.
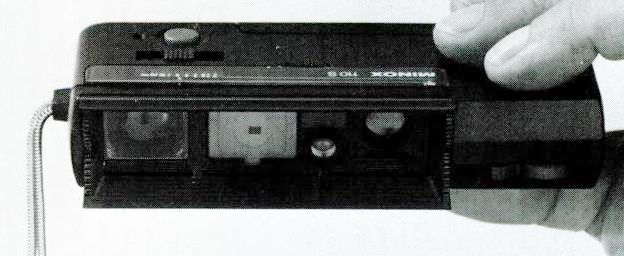
The image on the left shows the Minox in its open position, to allow use of the viewfinder, and the one on the right shows it in its closed position.
Before the war, Minox was produced by the company VEF in Latvia, starting from 1936. After the war, production of the Minox resumed in West Germany, by the new company Minox GmbH, founded by Walter Zapp, the original inventor of the Minox camera.
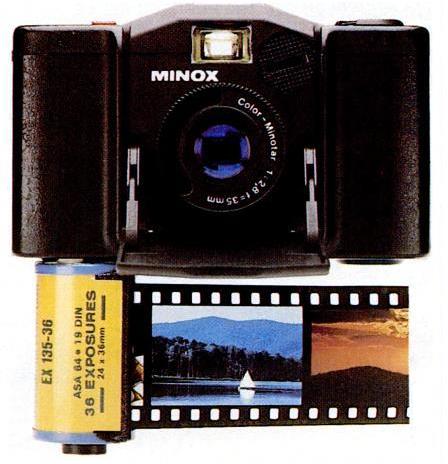

Later on, Minox branched out into making a compact and light camera that took full-frame photographs on conventional 35mm film. In fact, it made two models of this kind of camera, one of which was the Minox 35 EL shown at left.
Naturally, though, with their expertise and reputation for small cameras, they did not miss the opportunity to also make a camera using Kodak's new 110 film, the Minox 110S, shown at left.
On February 1, 1996, Kodak announced the new Advanced Photo System. This used film that was 24mm wide. The size of an image frame was 30.2mm by 16.7mm, but it could be optically indicated on the film that the desired print should instead only make use of a smaller area within that frame; two additional choices were available, 25.1mm by l6.7mm for a "classic" image in a shorter rectangle, or 30.2mm by 9.5mm for a "panoramic" image in a longer rectangle.
These sizes are known by the following abbreviations:
APS-H High Definition 30.2 mm by 16.7 mm APS-C Classic 25.1 mm by 16.7 mm APS-P Panoramic 30.2 mm by 9.5 mm
If you divide 25.1 by 16.7, the quotient is about 1.503. So the "classic" image is an attempt to match the 3:2 aspect ratio of 35mm SLRs, rather than an attempt to switch from an aspect ratio close to 3:2 to something more like the 7:6 ratio of many large format cameras, which is what I had been expecting at first.
The film speed was recorded magnetically on the film, and optionally cameras could record data magnetically on the film as well, such as an indication of how many frames had been exposed.
The life of this film format was, of course, cut short by the transition to digital photography. However, it left a mark on the era of digital phtography, as full-frame 36mm by 24mm sensors were expensive to make, many digital cameras aiming to be similar to 35mm SLRs used sensors the size of an APS-C frame instead, since that was the one which was similar to a standard 35 mm still picture frame in aspect ratio.
Even sensors of this size were still expensive, and so budget 35mm SLRs used sensors 17.6mm by 13.2mm, in the "four-thirds" size.
Incidentally, I recently read an article about how Canon, while full-frame sensors were still very expensive, tried to offer something better than an APS-C sensor by using APS-H sensors in several of their cameras in the EOS-1D series instead.
A note on the most common roll film formats may be in order here. A lot of sites give widths for the images made on many different film formats, but information on the actual width on the film is harder to find, I've seen.
Film type Film width Image width 112/115 7" 101 3 1/2" 122 92 mm 3 5/8" 3 1/4" 127 46 mm 1 13/16" 40mm 1 5/8" 116 70 mm 2 3/4" 2 1/2" 828 35 mm 1 3/8" 28mm 1 1/8" 120/220/620 61.5 mm 2 7/16" 60mm 2 1/4"
Just as 35mm film is 70mm film cut in half, apparently 122 roll film was exactly twice as wide as 127 roll film. 122 roll film is what the Pal Ko camera used, which was unique in being a view camera that used roll film, moving the film out of the way by rolling it up on the spool.
It was interesting to learn that what is now called 35mm film was originally specified by Thomas Edison in inches.
I think that 61.5 mm is closest to 2 7/16", but I've seen the width of that film in inches given as 2 2/5".